OJ 系统最大的难点在于 判题系统
项目介绍
用于在线评测编程题目代码的系统,能够根据用户提交的代码、出题人预先设置的题目输入和输出用例,进行编译
代码、运行代码、判断代码运行结果是否正确。
判题系统作为一个开放API提供给大家,便于开发者开发自己的O)系统。
初步需求
不能让用户随便引入包、随便遍历、暴力破解,需要使用正确的算法。=>安全性
判题过程是异步的=>异步化
提交之后,会生成一个提交记录,有运行的结果以及运行信息(时间限制、内存限制)
OJ 系统常用概念
ac表示你的题目通过,结果正确
题目限制:时间限制、内存限制
题目介绍
题目输入
题目输出
题目输入用例
题目输出用例
普通测评:比对用例文件,管理员设置题目的输入和输出用例,比如我输入1,你要输出2才是正确的;交给判题机去执行用户的代码,给用户的代码喂输入用例,比如1,看用户程序的执行结果是否和标准答案的输出一致。
特殊测评(SPJ):管理员设置题目的输入和输出,比如我输入1,用户的答案只要是 > 0 或 < 2 都是正确的;特定程序,不是通过比对用例文件是否一致这种死板程序来检验,而是专门为这道题目写一个判题程序。程序接收题目的输入(1)、标准输出用例(2)、用户的结果(1.5),特判程序根据这些值来比较是否正确。
交互测评:让用户输入一个例子,就给一个输出结果,交互比较灵活,没办法通过简单、死板的输入输出文件来搞定。
项目流程
- 项目介绍、项目调研、需求分析
- 核心业务流程
- 项目要做的功能(功能模块)
- 技术选型(技术预研)
- 项目初始化
- 项目开发
- 测试
- 优化
- 代码提交、代码审核
- 产品验收
- 上线
现有项目调研
https://github.com/HimitZH/HOJ(适合学习)
https://github.com/QingdaoU/OnlineJudge(python,不好学,很成熟)
https://github.com/hzxie/voj(星星没那么多,没那么成熟,但相对好学)
https:://github.com/vfleaking/uoj(php实现的)
https://github.com/zhblue/hustoj(成熟,但是php)
实现核心
1)权限校验
谁提交代码,谁不能提交代码
2)代码沙箱(安全沙箱)
用户代码藏毒:写个木马文件,修改系统权限
沙箱:隔离的、安全的环境,用户的代码不会影响到沙箱之外的系统的运行
资源分配:系统的内存就 2 个 G,用户疯狂占用系统资源,其他人用不了,甚至系统崩溃。因此要限制用户程序的占用资源。
3)判题规则
题目用例的比对,结果的验证
4)任务调度
服务器资源有限,用户要排队,按顺序去执行判题,而不是直接拒绝
核心业务流程
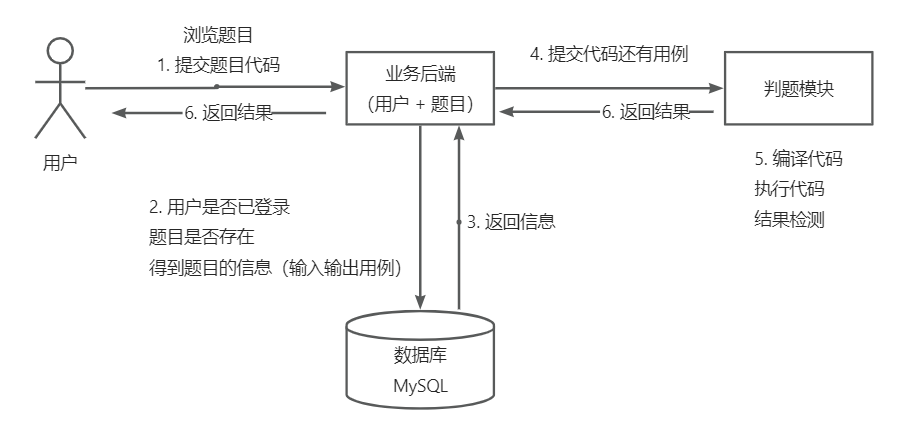
判题服务:获取题目信息,预计的输入输出结果,返回给主业务后端:用户的答案是否正确
代码沙箱:只负责运行代码,给出结果,不管什么结果是否正确
功能
题目模块
创建题目(管理员)
删除题目(管理员)
修改题目(管理员)
搜索题目(用户)
在线做题
提交题目代码
用户模块
注册
登录
判题模块
提交判断(结果是否正确)
错误处理(内存溢出、安全性、超时)
自主实现代码沙箱(安全沙箱)
开放接口(提供一个独立的新服务)
在线做题,在线提交
项目扩展思路
- 支持多种语言
- Remote Judge
- 完善的评测功能:普通测评、特殊测评、交互测评、在线自测、子任务分组评测、文件 IO
- 统计分析用户判题记录
- 权限校验
技术选型
前端:Vue3、Arco Desgin组件库、手撸项目模板、在线代码编辑器、在线文档浏览
Java 进程控制、Java安全管理器、部分 JVM 知识点
虚拟机(云服务器)、Docker(代码沙箱实现)
Spring Cloud 微服务、消息队列
主流的 OJ 实现方案
开发原则:能用比人现成的就用别人现成的
- 用现成的O)系统,比如judge0
https://github.com/judge0/judge0
自己用源码来部署、公有云、私有云
- 用现成的判题API(比如judge0),现成的代码沙箱
https://rapidapi.com/judge0-official/api/judge0-ce
实例接口参数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {
"language_id": 76,
"source_code": "I#include <stdio.h>\n\nint main(void) {\n char name[10];\n scanf(\"%s\", name);\n printf(\"hello, %s\n\", name);\n return 0;\n}",
"stdin": "Judge0",
"expected_output": "hello, Judge0"
}
|
- 自主开发
4)把 AI 当做代码沙箱
5)移花接木。你可以通过操作模拟浏览器的方式,用别人的 OJ 来帮你判题
前端初始化
全局状态管理
user.ts:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import { StoreOptions } from "vuex";
export default {
namespaced: true,
state : () => ({
loginUser: {
userName: '未登录',
},
}),
actions : {
async getLoginUser ({ commit, state }, payload) {
commit("updateUser", { userName: "C1own"});
},
},
mutations : {
updateUser (state, payload) {
state.loginUser = payload
},
}
} as StoreOptions<any>;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import { createStore } from 'vuex'
import user from './user';
export default createStore({
state: {
},
getters: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
user
}
})
|
获取状态变量:
1
2
| const store = useStore();
console.log(store.state.user.loginUser);
|
权限管理
我能够直接以一套通用的机制,去定义哪个页面需要哪些权限
思路:
- 在路由配置文件中,定义某个路由的访问权限
- 在全局页面组件中,绑定一个全局路由监听。每次访问页面时,根据用户要访问页面的路由信息,先判断用户是否有对应的访问权限。
- 如果有,就跳转到原页面;如果没有,拦截或跳转到 401 鉴权或登录页
优化页面布局
- 底部 footer 布局优化
- 优化 content、globalHeader 样式
- 优化导航栏用户名称的换行
通用导航栏组件 - 根据配置控制菜单的显隐
v-for 和 v-if 的优先级?
v-for 会先执行
1)给路由新增一个标志位,控制路由的显隐
2)不要用 v-for + v-if 去条件渲染元素,这样会渲染所有的数组,导致性能浪费
推荐:先过滤仅需要展示的数组。通过添加路由的 meta 信息,定义路由 hideInMenu 属性来控制是否隐藏,将路由数组过滤为 hideInMenu 数组。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <a-menu-item v-for="item in visibleRoutes" :key="item.path">
{{ item.name }}
</a-menu-item>
const visibleRoutes = routes.filter((item, index) => {
if (item.meta?.hideInMenu) {
return false;
}
return true;
});
|
根据权限隐藏菜单
需求:只有有权限的菜单,才对用户可见
原理:类似上面的控制路由的显示隐藏,只要判断用户有无权限即可
全局权限管理
- 定义权限
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
const accessEnum = {
NOT_LOGIN: "notLogin",
USER: "user",
ADMIN: "admin",
}
export default accessEnum;
|
- 定义一个通用的权限校验方法,因为菜单组件需要鉴权,权限拦截也需要鉴权,所有我们可以抽象出来
创建 checkAcces 文件,专门定义检测权限的函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
import ACCESS_ENUM from "@/access/accessEnum";
const checkAccess = (loginUser, needAccess = ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN)=> {
const loginUserAccess = loginUser?.userRole ?? ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN;
if (needAccess === ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN) {
return true;
}
if (needAccess === ACCESS_ENUM.USER) {
if (loginUserAccess === ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN) {
return false;
}
}
if (needAccess === ACCESS_ENUM.ADMIN) {
if (loginUserAccess !== ACCESS_ENUM.ADMIN) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
|
- 修改 GloablHeader 动态菜单组件,根据权限来过滤菜单
注意:这里使用计算属性,是为了当登录用户信息发生改变时,能够出发菜单栏的重新渲染,展示新增权限的菜单项。
全局项目入口
app.vue 中预留一个可以编写全局初始化逻辑的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
const doInit = () => {
console.log("hello 欢迎来到我的项目");
};
onMounted(() => {
doInit();
});
|
后端
前后端联调
前端和后端如何连接起来?接口 / 请求
1)安装请求工具 axios
2)编写调用后端的代码
传统情况,每个请求都要单独编写请求代码。
但现在我可以通过 https://github.com/ferdikoomen/openapi-typescript-codegen 自动生成前端请求代 码
安装命令
1
| npm install openapi-typescript-codegen --save-dev
|
生成前端请求接口的命令
1
| openapi --input http://localhost:8081/api/v2/api-docs --output ./generated --client axios
|
3)直接使用哼生成的 Service 代码,直接调用函数发送请求即可,比如获取登录信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
const res = await UserControllerService.getLoginUserUsingGet();
if (res?.code === 0) {
commit("updateUser", res.data);
} else {
commit("updateUser", {
...state.loginUser,
userRole: ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN
});
|
如果想要自定义请求参数,怎么办?
1)修改代码生成器提供的全局请求参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| export const OpenAPI: OpenAPIConfig = {
BASE: 'http://localhost:8081/api',
VERSION: '1.0',
WITH_CREDENTIALS: false,
CREDENTIALS: 'include',
TOKEN: undefined,
USERNAME: undefined,
PASSWORD: undefined,
HEADERS: undefined,
ENCODE_PATH: undefined,
};
|
2)修改 axios 的全局请求参数
用户登录功能
自动登录
1)在 store\user.ts 中编写获取远程调用用户登录信息的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| actions: {
async getLoginUser({ commit, state }, payload) {
const res = await UserControllerService.getLoginUserUsingGet();
if (res?.code === 0) {
commit("updateUser", res.data);
} else {
commit("updateUser", {
...state.loginUser,
userRole: ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN
});
}
},
},
|
2)在哪触发 getLoginUser 函数的执行?应当在一个全局的位置
有很多选择:
- 路由拦截
- 全局页面入口 app.vue
- 全局通用布局(所有页面都共享的组件)
全局权限管理优化
1)新建 access\index.ts 文件,把原有的路由拦截,权限校验逻辑放在独立的文件中
优势:只要不引入、就不会对项目有影响
2)编写权限管理逻辑和自动登录逻辑
如果没登录,则自动登录:
1
2
3
4
| if (!loginUser || !loginUser.userRole) {
await store.dispatch("user/getLoginUser");
}
|
3)如果用户访问的页面不需要登录,是否需要强制跳转到登录页?
答:不需要
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| const needAccess = (to.meta?.access as string) ?? ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN;
if (needAccess !== ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN) {
if (!loginUser || !loginUser.userRole) {
next(`/user/login?redirect=${to.fullPath}`);
return;
}
if (!checkAccess(loginUser, needAccess)) {
next('/noauth');
}
}
next();
|
完整代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| import router from "@/router";
import store from "@/store";
import ACCESS_ENUM from "@/access/accessEnum";
import checkAccess from "@/access/checkAccess";
router.beforeEach(async (to, from, next) => {
console.log("登录用户信息", store.state.user.loginUser);
const loginUser = store.state.user.loginUser;
if (!loginUser || !loginUser.userRole) {
await store.dispatch("user/getLoginUser");
}
const needAccess = (to.meta?.access as string) ?? ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN;
if (needAccess !== ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN) {
if (!loginUser || !loginUser.userRole) {
next(`/user/login?redirect=${to.fullPath}`);
return;
}
if (!checkAccess(loginUser, needAccess)) {
next('/noauth');
}
}
next();
});
|
支持多套布局
1)在 routes 路由文件中新建一套用户路由,使用 vue-router 自带的子路由机制,实现布局和嵌套
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| export const routes: Array<RouteRecordRaw> = [
{
path: "/user",
name: "用户",
component: UserLayout,
children: [
{
path: "/user/login",
name: "用户登录",
component: UserLoginView,
},
{
path: "/user/register",
name: "用户注册",
component: UserRegisterView,
},
]
},
{
path: "/",
name: "浏览题目",
component: HomeView,
},
{
path: "/hide",
name: "隐藏页面",
component: HomeView,
meta: {
hideInMenu: true,
}
},
{
path: "/noauth",
name: "无权限",
component: NoAuthPage,
},
{
path: "/admin",
name: "管理员可见",
component: AdminView,
meta: {
access: ACCESS_ENUM.ADMIN,
},
},
{
path: "/about",
name: "关于我的",
component: () =>
import("../views/AboutView.vue"),
},
];
|
2)新建 UserLayout、UserLoginView、UserRegisterView 页面,并且在 routes 中引入
3)在 app.vue 根页面文件,根据路由去区分多套布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <div id="app">
<template v-if="route.path.startsWith('/user')">
<router-view />
</template>
<template v-else>
<basic-layout />
</template>
</div>
|
当前这种 app.vue 中通过 if else 区分布局的方式不是最优雅的,理想的情况下直接读取 routes.ts,在这个文件中定义多套布局,然后自动使用页面布局
小扩展:实现上后面的思路
登录注册页面开发
登录页面:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| <template>
<div id="userLogin">
<h2 style="margin-bottom: 16px">用户登录</h2>
<a-form style="max-width: 480px; margin: 0 auto" :model="form" auto-label-width @submit="handleSubmit" label-align="right">
<a-form-item field="账号" tooltip="账号不少于4位" label="账号">
<a-input
v-model="form.userAccount"
placeholder="请输入账号"
/>
</a-form-item>
<a-form-item field="密码" label="密码" tooltip="密码不少于8位">
<a-input-password v-model="form.userPassword" placeholder="请输入密码" />
</a-form-item>
<a-form-item>
<a-button type="primary" html-type="submit" style="width: 120px; margin-left: 120px; border-radius: 5%; margin-top: 10px">登录</a-button>
</a-form-item>
</a-form>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { reactive } from "vue";
import { UserControllerService } from "../../../generated";
import message from '@arco-design/web-vue/es/message';
import { useRouter } from "vue-router";
import store from "@/store";
const router = useRouter();
const form = reactive({
userAccount: '',
userPassword: '',
});
const handleSubmit = async () => {
const res = await UserControllerService.userLoginUsingPost(form);
if (res?.code === 0) {
await store.dispatch('user/getLoginUser');
message.success('登录成功');
// 跳转到主页
router.push({
path: '/',
replace: true,
});
} else {
message.error('登录失败' + (res.message ? `,${res.message}` : ''));
}
};
</script>
|
注册页面:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| <template>
<div id="userRegister">
<h2 style="margin-bottom: 16px; margin-left: 40px">用户注册</h2>
<a-form
style="max-width: 480px; margin: 0 auto"
:model="form"
auto-label-width
@submit="handleSubmit"
label-align="right"
>
<a-form-item field="账号" tooltip="账号不少于4位" label="账号">
<a-input v-model="form.userAccount" placeholder="请输入账号" />
</a-form-item>
<a-form-item field="密码" label="密码" tooltip="密码不少于8位">
<a-input-password
v-model="form.userPassword"
placeholder="请输入密码"
/>
</a-form-item>
<a-form-item
field="确认密码"
label="确认密码"
tooltip="确认密码不少于8位"
>
<a-input-password
v-model="form.checkPassword"
placeholder="请输入确认密码"
/>
</a-form-item>
<a-form-item>
<a-button
type="primary"
html-type="submit"
style="
width: 120px;
margin-left: 120px;
border-radius: 5%;
margin-top: 10px;
"
>注册</a-button
>
</a-form-item>
</a-form>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { reactive } from "vue";
import { UserControllerService } from "../../../generated";
import message from "@arco-design/web-vue/es/message";
import { useRouter } from "vue-router";
const router = useRouter();
const form = reactive({
userAccount: "",
userPassword: "",
checkPassword: "",
});
const handleSubmit = async () => {
const res = await UserControllerService.userRegisterUsingPost(form);
if (res?.code === 0) {
message.success("注册成功");
// 跳转到主页
router.push({
path: "/user/login",
replace: true,
});
} else {
message.error("注册失败" + (res.message ? `,${res.message}` : ""));
}
};
</script>
|
数据库表设计
题目表
题目标题
题目内容:存放题目的介绍、输入输出提示、描述、具体的事情
题目标签:栈、队列、链表、简单、中等、困难
题目答案:管理员/用户设置的标准答案
提交数、通过题目的人数:便于统计分析(可以考虑自动给题目打难易度标签)
判题先关字段:
如果说题目不是很复杂,用例文件大小不大的话可以存在数据库中
但如果用例文件比较大,> 512 KB 建议单独存放在一个文件中,数据库中只保存 url(类似存储用户头像)
- 输入用例:1、2
- 输出用例:3、4
- 时间限制
- 内存限制
judgeConfig 判题配置(json 对象):
时间限制 timeLimit
内存限制 memoryLimit
堆栈限制 stackLimit
judgeCase 判题用例(json 数组):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| [
{
"input": "1 2",
"output": "3 4"
},
{
"input": "1 2",
"output": "2 4"
}
]
|
小知识
json 小知识
存 json 的好处:便于维护和扩展
使用场景:
- 一般不根据 json 的内容查询数据库,不倒查
- 字段含义相关,属于同一类值
- 你的字段存储空间占用不能太大
什么时候适合加索引?如何选择给哪个字段加索引?
答:首先从业务出发,无论是当个索引、还是联合索引,都要从你实际的查询语句、字段枚举值的区分度、字段的类型考虑(where 条件指定的字段)
比如:where userId = 1 and question = 2
可以选择加两个单独索引,也可以选择给两个字段建联合索引。当查询时两个字段都要查,就用联合索引。原则上越简单越好,能不用索引就不用,能用单个就用单个索引,毕竟索引也会占用空间;不要给没区分度的字段加索引(比如性别)
题目表 DDL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| create table if not exists question
(
id bigint auto_increment comment 'id' primary key,
title varchar(512) null comment '标题',
content text null comment '内容',
tags varchar(1024) null comment '标签列表(json 数组)',
answer text default 0 not null comment '题目答案',
submitNum int default 0 not null comment '提交人数',
accessNum int default 0 not null comment '通过人数',
judgeCase text null comment '判题用例(json 数组)',
judgeConfig text null comment '判题配置(json 对象)',
thumbNum int default 0 not null comment '点赞数',
favourNum int default 0 not null comment '收藏数',
userId bigint not null comment '创建用户 id',
createTime datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null comment '创建时间',
updateTime datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP comment '更新时间',
isDelete tinyint default 0 not null comment '是否删除',
index idx_userId (userId)
) comment '帖子' collate = utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
|
题目提交表
哪个用户写了哪道题,存放判题结果等
提交用户 id:userId
题目id:questionId
语言:language
状态:status(0 - 待判题,1 - 判题中,2 - 成功,3 - 失败)
判题信息(判题过程中得到一些信息,比如程序失败的原因,程序执行消耗的空间时间):
judgeInfo(json 对象)
1
2
3
4
5
| {
"message":"程序执行信息",
"time": 1000,
"memory": 1000
}
|
判题信息枚举值:
- Accepted 成功
- Wrong Answer 答案错误
- Compiled Error 编译失败
- Memory Limit Exceeded 内存溢出
- Time Limit Exceeded 超时
- Prenestation Error 展示错误
- Output Limit Exceeded 输出溢出
- Waiting 等待中
- Dangerous Operation 危险操作
- RunTime Error 运行错误(用户程序问题)
- System Error 系统错误(做系统人的问题)
后端接口开发
后端开发流程
- 根据功能设计库表
2 )自动生成对数据库基本的增删改查(mapper和service层的基本功能)
- 编写Controller层,实现基本的增删改查和权限校验(复制粘贴)
- 去根据业务定制开发新的功能/编写新的代码
更好的办法,编写自己的代码生成器((https://github.com/liyupi/sql-father-frontend-public)
为了更方便处理 json 字段中的某个字段,需要给对应的字段编写特殊的类,如 JudgeConfig、JudgeInfo、JudgeCase。
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
@Data
public class JudgeCase implements Serializable {
private String input;
private String output;
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
}
|
什么情况下要加业务前缀?什么情况下不加?
加的好处:防止多个表都有类似的类,产生冲突;不加的前提:可能这个类是多个业务之间是共享的
编写好基本代码后,通过 swagger 或者单元测试进行代码测试
查询提交信息接口
功能:能够根据用户 id、或者题目 id、编程语言,去查询提交记录
注意事项:仅本人能看见自己提交代码的答案、提交代码
实现方案:
先查询,再根据权限进行脱敏
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Override
public QuestionSubmitVO getQuestionSubmitVO(QuestionSubmit questionSubmit, User loginUser) {
QuestionSubmitVO questionSubmitVO = QuestionSubmitVO.objToVo(questionSubmit);
Long userId = loginUser.getId();
if (userId != questionSubmit.getUserId() && !userService.isAdmin(loginUser)) {
questionSubmitVO.setCode(null);
}
return questionSubmitVO;
}
|
前端开发
1)用户注册页面
2)创建题目页面(管理员)
3)题目管理页面(管理员)
4)题目列表页(用户)
5)题目详情页(在线做题页)
6)题目提交列表页
接入要用的组件
先接入要用的组件,再去写页面,防止后续因为冲突导致依赖冲突、整合组件带来的冲突
Markdown 编辑器
为什么用 Markdown?
一套通用的文本编辑语法,简单易学。可以在各大网站上渲染统一的样式
推荐的在线编辑器
ByteMD:https://github.com/bytedance/bytemd
安装命令:
在 main.ts 文件中引入
1
| import 'bytemd/dist/index.css'
|
新建一个 MdEditor 组件,并安装高亮和 gfm 插件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| npm -i @bytemd/plugin-highlight
npm -i @bytemd/plugin-gfm
<template>
<Editor
:value="value"
:mode="mode"
:plugins="plugins"
@change="handleChange"
/>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import gfm from "@bytemd/plugin-gfm";
import highlight from "@bytemd/plugin-highlight";
import { Editor } from "@bytemd/vue-next";
import { defineProps, withDefaults } from "vue";
interface Props {
value: string;
mode: string;
handleChange: (v: string) => void;
}
const plugins = [gfm(), highlight()];
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
value: () => "",
mode: () => "split",
handleChange: (v: string) => {
console.log(v);
},
});
</script>
<style>
.bytemd-toolbar-icon.bytemd-tippy.bytemd-tippy-right:last-child {
display: none;
}
</style>
|
隐藏编辑器不需要的图标
1
2
3
| bytemd-toolbar-icon bytemd-tippy bytemd-tippy-right:last_child svg {
display: none;
}
|
要把 MdEditor 当前输入的值暴露给父组件,便于父组件去使用,同时也是提高组件的通用性,把 value 和 handleChange 交给父组件去管理
去除 github 图标
1
2
3
| .bytemd-toolbar-icon.bytemd-tippy.bytemd-tippy-right:last-child {
display: none;
}
|
代码编辑器
微软官方:Monaco Editor (https://github.com/microsoft/monaco-editor 官方整合教程)
项目拓展:diff editor 用户代码和答案代码对比
1)安装命令:
1
| npm install monaco-editor
|
2)打包插件,便于打包和整合(https://github.com/microsoft/monaco-editor/tree/main/webpack-plugin)
1
| npm install monaco-editor-webpack-plugin
|
3)vue-cli/webpack 项目整合 Monaco Editor(官方整合教程: )
)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| const { defineConfig } = require("@vue/cli-service");
const MonacoWebpackPlugin = require("monaco-editor-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = defineConfig({
transpileDependencies: true,
chainWebpack(config) {
config.plugin(new MonacoWebpackPlugin({}));
},
});
|
如何使用 Monaco editor?查看示例教程:
https://microsoft.github.io/monaco-editor/playground.html?source=v0.40.0#example-creating-the-editor-hello-world chart.zhenglinglu.cn/pages/,2244hbd/#在-vue-中使用
报错:ERROR in ./node_modules/monaco-editor/esm/vs/language/typescript/tsMode.js
解决方法:
https://blog.csdn.net/laisy334514/article/details/120807375
注意,manaco editor 在读写值的时候,要使用 toRaw(编辑器实例)的语法来操作,否则会卡死
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| <template>
<div id="container" ref="codeEditorRef" style="min-height: 400px"></div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import * as monaco from "monaco-editor";
import { onMounted, ref, toRaw, withDefaults, defineProps } from "vue";
/**
* 定义组件属性类型
*/
interface Props {
value: string;
handleChange: (v: string) => void;
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
value: () => "",
handleChange: (v: string) => {
console.log(v);
},
});
const codeEditorRef = ref();
const codeEditor = ref();
onMounted(() => {
if (!codeEditorRef.value) {
return;
}
codeEditor.value = monaco.editor.create(codeEditorRef.value, {
value: props.value,
language: "java",
automaticLayout: true,
minimap: {
enabled: true,
},
readOnly: false,
theme: "vs-dark",
});
// 编辑 监听内容变化
codeEditor.value.onDidChangeModelContent(() => {
props.handleChange(toRaw(codeEditor.value).getValue());
})
});
</script>
<style scoped></style>
|
解决 ResizeObserver loop completed with undelivered notifications.at handleError (webpack-internal:///./node_modules/webpack-dev-server/client/overlay.js:299:58) at eval (webpack-internal:///./node_modules/webpack-dev-server/client/overlay.js:318:7) 报错
在 main.ts 或者 app.vue 添加如下代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| const debounce = (fn, delay) => {
let timer
return (...args) => {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer)
}
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn(...args)
}, delay)
}
}
const _ResizeObserver = window.ResizeObserver;
window.ResizeObserver = class ResizeObserver extends _ResizeObserver{
constructor(callback) {
callback = debounce(callback, 200);
super(callback);
}
}
|
同 md 编辑器一样,也要接受父组件的传值,把显示的输入交给父组件去控制,从而能够让父组件实时得到用户实时输入的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| interface Props {
value: string;
handleChange: (v: string) => void;
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
value: () => "",
handleChange: (v: string) => {
console.log(v);
},
});
|
重新生成前端请求代码
重新生成代码是要将 WITH_CREDENTIALS 改为 true,不然登录后请求会不携带 cookie
1
| openapi --input http://localhost:8081/api/v2/api-docs --output ./generated --client axios
|
管理员添加题目需要输入的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| {
"answer": "二分 + 暴力破解",
"content": "题目内容",
"judgeCase": [
{
"input": "1 2",
"output": "3 4"
}
],
"judgeConfig": {
"memoryLimit": 1000,
"stackLimit": 1000,
"timeLimit": 1000
},
"tags": [
"二分","中等"
],
"title": "A + B + C"
}
|
注意,我们自定义的代码编辑器组件不会被组件库识别,需要手动指定 value 和 handleChange 函数
题目管理页面开发
1)使用表格组件:https://arco.design/vue/component/table#custom(找到可以自定义操作的表格)
2)查询数据
3)定义表格列
4)加载数据
5)调整格式
比如 json 格式不好看,有两个方法调整:
- 使用组件库自带的语法,自动格式化
- 完全自定义渲染,想展示什么就展示什么
删除表格元素如何实现动态显示删除过程/结果
更新页面开发
策略:由于更新和创建都是相同的表单,所以完全没必要开/复制2遍,可以直接复用创建页面。
关键实现:如何区分两个页面?
- 路由(/add/question和/update/question)
- 请求参数(id=1)
更新页面相比于创建页面,多了两个改动:
- 页面加载时,要加载出需要修改的数据
- 点击修改按钮时,请求地址不同
当前代码优化
1)处理菜单项的权限控制和显示隐藏
2)管理页面分页问题的修复
可以参考聚合搜索项目的搜索条件改变和 url 改变状态同步
核心原理:在分页号改变时,触发事件改变 searchParams 的值,并且通过 watchEffect 监听 searchParams 的改变(然后执行 loadData 重新加载),实现了页号变化时触发页面的重现加载。
3)修复刷新页面未登录问题
原 store\user.ts 文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| import { StoreOptions } from "vuex";
import ACCESS_ENUM from "@/access/accessEnum";
import { UserControllerService } from "../../generated";
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: () => ({
loginUser: {
userName: "未登录",
userRole: ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN
},
}),
actions: {
async getLoginUser({ commit, state }, payload) {
const res = await UserControllerService.getLoginUserUsingGet();
if (res?.code === 0) {
commit("updateUser", res.data);
} else {
commit("updateUser", {
...state.loginUser,
userRole: ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN
});
}
},
},
mutations: {
updateUser(state, payload) {
state.loginUser = payload;
},
},
} as StoreOptions<any>;
|
修改后的 store\user.ts 文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| import { StoreOptions } from "vuex";
import ACCESS_ENUM from "@/access/accessEnum";
import { UserControllerService } from "../../generated";
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: () => ({
loginUser: {
userName: "未登录",
userRole: ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN
},
isLoading: false
}),
actions: {
async getLoginUser({ commit, state }) {
try {
commit("setLoading", true);
const res = await UserControllerService.getLoginUserUsingGet();
if (res?.code === 0) {
commit("updateUser", res.data);
} else {
commit("updateUser", {
...state.loginUser,
userRole: ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN
});
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to get user data:", error);
commit("updateUser", {
...state.loginUser,
userRole: ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN
});
} finally {
commit("setLoading", false);
}
},
},
mutations: {
updateUser(state, payload) {
console.log("Updating state with:", payload);
state.loginUser = payload;
},
setLoading(state, payload) {
state.isLoading = payload;
}
},
} as StoreOptions<any>;
|
修改 access\index.ts 文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| import router from "@/router";
import store from "@/store";
import ACCESS_ENUM from "@/access/accessEnum";
import checkAccess from "@/access/checkAccess";
router.beforeEach(async (to, from, next) => {
console.log("当前登录用户信息", store.state.user.loginUser);
let loginUser = store.state.user.loginUser;
if (!loginUser || !loginUser.userRole) {
await store.dispatch("user/getLoginUser");
loginUser = store.state.user.loginUser;
console.log("更新后的登录用户信息", loginUser);
}
const needAccess = (to.meta?.access as string) ?? ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN;
if (needAccess !== ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN) {
if (!loginUser || !loginUser.userRole) {
next(`/user/login?redirect=${to.fullPath}`);
return;
}
if (!checkAccess(loginUser, needAccess)) {
next('/noauth');
return;
}
}
next();
});
|
题目浏览页
1)复制管理题目页的表格
2)只保留需要的columns字段
3)自定义表格列的渲染
标签:使用 tag 组件
通过率:自行计算
前段使用 moment 库对创建时间进行格式处理(https://momentjs.cn/docs/#/displaying/)
操作按钮:补充跳转到做题页的按钮
5)编写搜索表单,使用 form 的 layout 的 inline 布局,让用户的输入和 searchParams 同步,
题目列表搜索页
做题页面
1)先定义动态参数路由,开启 props 为 true,可以在页面的 props 中直接获取到动态参数(题目 id)
2)定义布局:左侧是题目信息,右侧是代码编辑器
在代码编辑器中监听属性的变化,注意监听 props 要使用箭头函数
3)左侧题目信息:
- tabs 切换展示的内容
- 定义 MdViewer 组件展示题目内容
- 使用 description 展示判题配置
4)使用 select 组件让用户选择编程语言
在代码编辑器中监听属性的变化,注意监听pops要使用箭头函数
https://blog.csdn.net/wuyxinu/article/details/124477647
后端判题模块预开发
目的:跑通完整的业务流程
梳理判题模块和代码沙箱的关系
判题模块:调用代码沙箱,把代码和输入交给代码沙箱去执行
代码沙箱:只负责接收代码和输入,返回编译运行的结果,不负责判题(可以作为独立的项目/服务,提供给其他需要执行代码的项目去使用)
这两个模块完全解耦
大致流程:判题模块发送代码和输入用例给代码沙箱,代码沙箱根据这些执行代码,并将执行结果和相关占用资源信息返回给判题模块,判题模块根据这些进行判断,看结果是否正确或者是否超时、OOM(二者通过 API 交互,实现解耦)
思考:为什么代码沙箱要接受和输出一组运行用例?
前提:我们每道题目有多组测试用例。
如果我们每个用例单独调用一次代码沙箱,会调用多次接口,需要多次网络传输、程序要多次编译、记录程序的执行状态(重复的代码不重复编译)
这是一种很常见性能优化方法!(批处理)
Lombok Builder 注解
实体类上加上:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ExecuteCodeRequest {
private List<String> inputList;
private String code;
private String language;
}
|
可以使用链式的方式更方便地给对象赋值
1
2
3
4
5
| ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest = ExecuteCodeRequest.builder()
.code(code)
.language(language)
.inputList(inputList)
.build();
|
代码沙箱开发
1)定义代码沙箱的接口,提高通用性
之后我们的项目代码只调用接口,不调用具体的实现类,这样在你使用其他的代码沙箱实现类时,就不用去修改名
称了,便于扩展。
代码沙箱请求接口中,timeLimit 可加可不,可自定扩展,即时中断程序
扩展思路:增加一个查看代码沙箱状态的接口
2)定义多种不同的代码沙箱实现
- 示例代码沙箱:仅为了跑通业务流程
- 远程代码沙箱:实际调用接口的沙箱
- 第三方代码沙箱:调用第三方的代码沙箱,https://github.com/criyle/go-judge
3)编写单元测试,验证单个代码沙箱的执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| @SpringBootTest
public class CodeSandboxTest {
@Test
void executeCode() {
CodeSandbox codeSandbox = new ExampleCodeSandbox();
String code = "int main {}";
String language = QuestionSubmitLanguageEnum.C.getValue();
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("1 2", "3 4");
ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest = ExecuteCodeRequest.builder()
.code(code)
.language(language)
.inputList(inputList)
.build();
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = codeSandbox.executeCode(executeCodeRequest);
Assertions.assertNotNull(executeCodeResponse);
}
}
|
但是现在的问题是,我们把 new 某个对象的代码写死了,如果后面的项目要改用其他沙箱,可能要改进很多地方的代码
4)使用工厂模式,根据用户传入的字符串参数来生成对应的代码沙箱实现类。
此处使用静态工厂
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public class CodeSandboxFactory {
public static CodeSandbox newInstance(String type) {
switch (type) {
case "example":
return new ExampleCodeSandbox();
case "remote":
return new RemoteCodeSandbox();
case "thirdParty":
return new ThirdPartyCodeSandbox();
default:
return new ExampleCodeSandbox();
}
}
}
|
扩展思路:如果确定代码示例不会出现线程安全问题、可复用,那么可以使用单例工厂模式
由此我们可以根据字符串参数调用不同的沙箱示例,提高代码通用性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
String type = scanner.next();
CodeSandbox codeSandbox = CodeSandboxFactory.newInstance(type);
String code = "int main {}";
String language = QuestionSubmitLanguageEnum.C.getValue();
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("1 2", "3 4");
ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest = ExecuteCodeRequest.builder()
.code(code)
.language(language)
.inputList(inputList)
.build();
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = codeSandbox.executeCode(executeCodeRequest);
}
}
|
5)参数配置化,把项目中一些自定义选项给用户在配置文件中配置。这样开发者只需要改配置文件,就能够自定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
codesanbox:
type: example
@SpringBootTest
public class CodeSandboxTest {
@Value("${codesandbox.type:example}")
String type;
@Test
void executeCode() {
CodeSandbox codeSandbox = CodeSandboxFactory.newInstance(type);
String code = "int main {}";
String language = QuestionSubmitLanguageEnum.C.getValue();
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("1 2", "3 4");
ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest = ExecuteCodeRequest.builder()
.code(code)
.language(language)
.inputList(inputList)
.build();
}
}
|
6)代码沙箱能力增强
比如:我们需要在调用代码沙箱前,输出请求参数日志;在代码沙箱调用后,输出响应结果日志,便于管理员去分析。
每个代码沙箱实现类都写一遍 log.info?难道每次调用代码沙箱都执行 log?
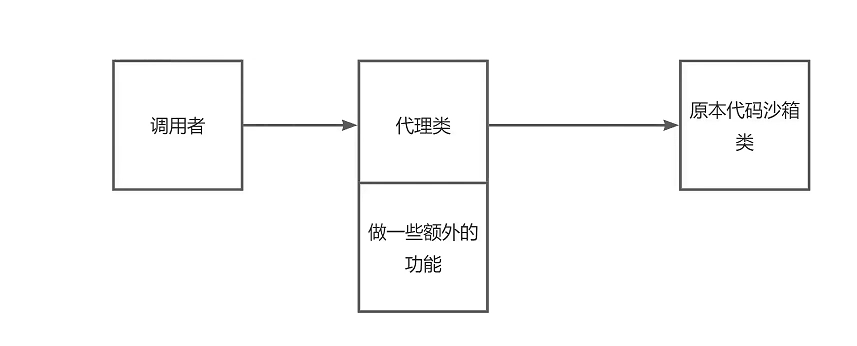
使用代码模式,提供一个 Proxy 类来增强代码沙箱的功能。
使用代理后:不仅没有改变原有的代码沙箱实现类,而且对调用者来说,调用方式几乎没有改变,也不需要在每个调用沙箱的地方去编写统计代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @Slf4j
public class CodeSandboxProxy implements CodeSandbox {
private final CodeSandbox codeSandbox;
public CodeSandboxProxy(CodeSandbox codeSandbox) {
this.codeSandbox = codeSandbox;
}
@Override
public ExecuteCodeResponse executeCode(ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest) {
log.info("代码沙箱请求信息:" + executeCodeRequest.toString());
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = codeSandbox.executeCode(executeCodeRequest);
log.info("代码沙箱响应信息:" + executeCodeResponse.toString());
return executeCodeResponse;
}
}
|
代理模式的作用:增强能力
7)实现示例代码沙箱
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public class ExampleCodeSandbox implements CodeSandbox {
@Override
public ExecuteCodeResponse executeCode(ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest) {
List<String> inputList = executeCodeRequest.getInputList();;
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = new ExecuteCodeResponse();
executeCodeResponse.setOutputList(inputList);
executeCodeResponse.setMessage("测试执行成功");
executeCodeResponse.setStatus(QuestionSubmitStatusEnum.SUCCEED.getValue());
JudgeInfo judgeInfo = new JudgeInfo();
judgeInfo.setMessage(JudgeInfoMessageEnum.ACCEPTED.getText());
judgeInfo.setMemory(100L);
judgeInfo.setTime(100L);
executeCodeResponse.setJudgeInfo(judgeInfo);
return executeCodeResponse;
}
}
|
判题服务完整业务流程实现
判题服务业务流程:
1)传入题目的提交 id,获取对应的题目、提交信息(包含代码,编程语言等)
2)如果题目的提交状态不是等待中,就不用重复执行了
3)更改题目提交的状态为“判题中”
4)调用沙箱,获取执行结果
5)根据沙箱的执行结果,设置题目的判题状态和信息
判断逻辑:
- 先判断沙箱执行的结果输出数量和预期输出数量相等
- 依次判断每一项输出和预期输出是否相等
- 判题题目的限制是否符合要求
- 可能还有其他的异常情况
策略模式优化判题代码
我们程序的判题策略可能会有很多种,比如:我们的代码沙箱本身执行的程序需要消耗时间,这个时间因不同的编程语言而异,比如沙箱执行 Java 要额外花 10 秒。
我们可以采用策略模式,针对不同的情况,定义独立的策略,而不是把所有的判题逻辑,if else 代码混在一起写
如果选择某种判题策略的过程比较复杂,都写在调用判题服务的代码中,代码会越来越复杂,会有很多 if else 代码,所以建议单独编写一个判断策略的类
1
2
3
4
5
| JudgeStrategy judgeStrategy = new DefaultJudgeStrategy();
if ("java".equals(language)) {
judgeStrategy = new JavaLanguageJudgeStrategy();
}
return judgeStrategy.doJudge(judgeContext);
|
定义 JudgeManager,目的是尽量简化对判题功能的调用,让调用方最简单
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Service
public class JudgeManager {
JudgeInfo doJudge(JudgeContext judgeContext) {
String language = judgeContext.getQuestionSubmit().getLanguage();
JudgeStrategy judgeStrategy = new DefaultJudgeStrategy();
if ("java".equals(language)) {
judgeStrategy = new JavaLanguageJudgeStrategy();
}
return judgeStrategy.doJudge(judgeContext);
}
}
|
- 历史问题修复
历史问题修复
代码编辑器切换语言失败问题
解决:监听 language 属性,动态更改编辑器的语言
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| watch(
() => props.language,
() => {
if (codeEditor.value) {
monaco.editor.setModelLanguage(
toRaw(codeEditor.value).getModel(),
props.language
);
}
}
);
|
代码沙箱实现
代码沙箱:只负责接受代码和输入,返回编译运行的结果,不负责判题(可以作为独立的项目/服务,提供给其
他的需要执行代码的项目去使用)
编写测试接口,验证能否访问
Java 原生实现代码沙箱
原生:尽可能不借助第三方库和依赖,用最干净、最原始的方式实现代码沙箱
代码沙箱需要:接受代码 => 编译代码(javac) => 执行代码(java)
编写实例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class SimpleCompute {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
Integer b = Integer.valueOf(args[1]);
System.out.println("结果" + (a + b));
}
}
|
编译代码:
1
| javac SimpleCompute.java
|
执行代码:
1
| java -cp . SimpleCompute 1 2
|
通过 chcp 命令查看编码,GBK 是 936,UTF-8 是 65001
chcp 查看和更改编码
javac 更改编吗
1
| javac -Dfile.encoding utf-8 SimpleCompute.java
|
实际 OJ 系统中,对用户输入的代码会有一定的要求,便于系统统一的处理。所以此处,我们把用户输入代码的类名限制为 Main(参考 Poj),可以减少类名不一致的风险,而且不用从用户代码中提取类名
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
Integer b = Integer.valueOf(args[1]);
System.out.println("结果" + (a + b));
}
}
|
核心流程实现
核心实现思路:用程序代替人工,用程序来操作命令行,去编译执行代码
Process:Java 进程执行管理类
- 把用户代码保存为文件
- 编译代码,得到 class 文件
- 执行代码,得到输出结果
- 收集整理输出结果
- 文件清理
- 错误处理,提升程序健壮性
1.把用户代码保存为文件
引入 hutool 工具类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.8.8</version>
</dependency>
|
2.编译代码,得到 class 文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String globalCodePathName = userDir + File.separator + GLOBAL_CODE_DIR_NAME;
if (!FileUtil.exist(globalCodePathName)) {
FileUtil.mkdir(globalCodePathName);
}
String userCodeParentPath = globalCodePathName + File.separator + UUID.randomUUID();
File userCodeFile = FileUtil.writeString(code, userCodeParentPath + File.separator + GLOBAL_JAVA_CLASS_NAME,
StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
String compileCmd = String.format("javac -encoding utf-8 %s", userCodeFile.getAbsolutePath());
try {
Process compileProcess = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(compileCmd);
int exitValue = compileProcess.waitFor();
if (exitValue == 0) {
System.out.println("编译成功");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(compileProcess.getInputStream()));
String compileOutputLine;
while ((compileOutputLine = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuilder.append(compileOutputLine);
}
} else {
System.out.println("编译失败,错误码:" + exitValue);
BufferedReader errorBufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(compileProcess.getErrorStream()));
String compileOutputLine;
while ((compileOutputLine = errorBufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuilder.append(compileOutputLine);
}
}
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
|
编写一个工具类,执行进程,获取
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public class ProcessUtils {
public static ExecuteMessage runProcessAndGetMessage(Process runProcess, String operation) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
ExecuteMessage executeMessage = new ExecuteMessage();
try {
int exitValue = runProcess.waitFor();
if (exitValue == 0) {
System.out.println(operation + "成功");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(runProcess.getInputStream()));
String compileOutputLine;
while ((compileOutputLine = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuilder.append(compileOutputLine);
}
executeMessage.setMessage(stringBuilder.toString());
} else {
System.out.println(operation + "失败,错误码:" + exitValue);
BufferedReader errorBufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(runProcess.getErrorStream()));
String compileOutputLine;
while ((compileOutputLine = errorBufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuilder.append(compileOutputLine);
}
executeMessage.setErrorMessage(stringBuilder.toString());
}
return executeMessage;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|
3.执行程序
同样是
1
| String compileCmd = String.format("javac -Dfile.encoding utf-8 %s", userCodeFile.getAbsolutePath());
|
很多 OJ 都是 ACM 模式,需要和用户交互,让用户不断输入内容并获取输出
注意关闭程序的输入输出流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| public static ExecuteMessage runInterProcessAndGetMessage(Process runProcess, String operationName, String args) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
ExecuteMessage executeMessage = new ExecuteMessage();
try {
OutputStream outputStream = runProcess.getOutputStream();
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream);
String[] s = args.split(" ");
outputStreamWriter.write(StrUtil.join("\n", s) + "\n");
outputStreamWriter.flush();
InputStream inputStream = runProcess.getInputStream();
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
String compileOutputLine;
while ((compileOutputLine = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuilder.append(compileOutputLine);
}
executeMessage.setMessage(stringBuilder.toString());
outputStream.close();
outputStreamWriter.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return executeMessage;
}
|
4.整理输出
获取程序执行时间:
1
2
3
4
| StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
stopWatch.stop();
stopWatch.getLastTaskTimeMillis()
|
此处我们使用最大值来统计时间:
扩展:可以每个测试用例都有一个独立的内存、时间占用的统计
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| long maxTime = 0;
for (ExecuteMessage executeMessage : executeMessageList) {
String errorMessage = executeMessage.getErrorMessage();
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(errorMessage)) {
executeCodeResponse.setMessage(errorMessage);
executeCodeResponse.setStatus(3);
break;
}
outputList.add(executeMessage.getMessage());
Long time = executeMessage.getTime();
maxTime = Math.max(maxTime, time);
}
|
要借助第三方库获取 Java Process 类的内存,非常麻烦
5.文件清理
1
2
3
4
| if (userCodeFile.getParentFile() != null) {
boolean del = FileUtil.del(userCodeParentPath);
System.out.println("删除" + (del ? "成功" : "删除"));
}
|
6.错误处理
封装一个错误处理方法,当程序出现异常返回错误响应
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
private ExecuteCodeResponse getErrorResponse(Throwable e) {
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = new ExecuteCodeResponse();
executeCodeResponse.setOutputList(new ArrayList<>());
executeCodeResponse.setMessage(e.getMessage());
executeCodeResponse.setStatus(2);
executeCodeResponse.setJudgeInfo(new JudgeInfo());
return executeCodeResponse;
}
}
|
异常情况演示
到目前为止,核心流程已经实现,但是要上线的话,安全么?
用户提交恶意代码怎么办?
1)执行阻塞,占用资源不释放 时间上搞你
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import lombok.SneakyThrows;
public class Main {
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
long ONE_HOUR = 60 * 60 * 100L;
Thread.sleep(ONE_HOUR);
System.out.println("睡完了");
}
}
|
要把写好的代码复制到 resource 目录下,并且把类名改为 Main!包名一定要去掉
2)占用内存,不释放
空间上搞你
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MemoryError {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
list.add(new byte[10000]);
}
}
}
|
3)读文件,信息泄露

 )
)


